2018-2019 Catalog: July 2018 Edition [ARCHIVED]
Mathematics
|
|
 Return to: Program, Degree and Certificate List Return to: Program, Degree and Certificate List
Dean: Lianna Zhao, MD
Academic Co-Chairs: Brett Monte, PhD; Lan Pham, PhD
Faculty: Miriam Castroconde; Carlo Chan, PhD; Terry Cheng; Joshua Danufsky; RJ Dolbin, PhD; Ilknur Erbas‑White; Catherine Famiglietti, PhD; Sanjai Gupta, PhD; Kenn Huber, PhD; Brent Monte, PhD; Lan Pham, PhD; Joel Sheldon; Benjamin Vargas, PhD; Richard Zucker
Courses
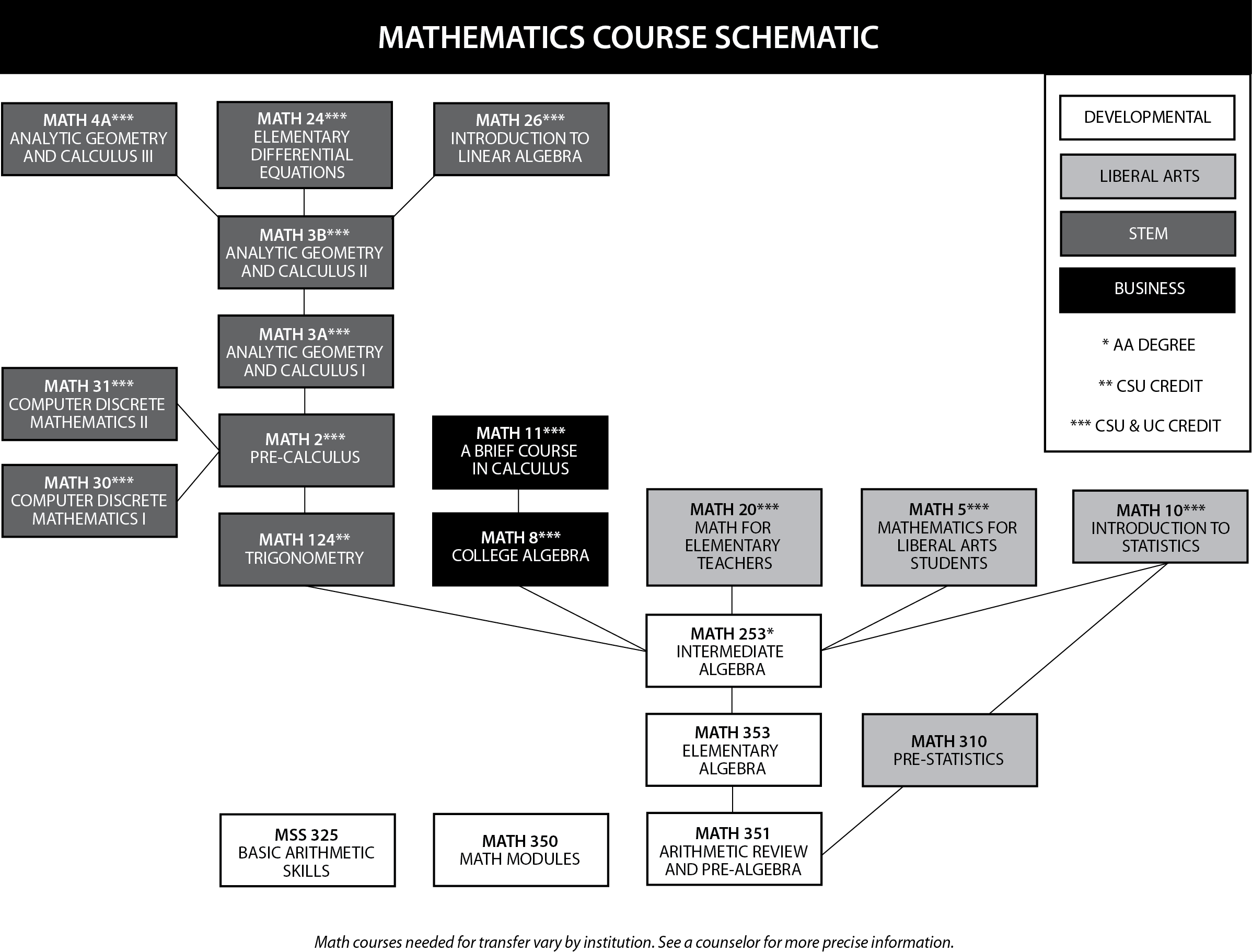
The Mathematics Department at Irvine Valley College offers a wide range of courses to meet the varied needs of students pursuing their academic and vocational goals. The department offers a comprehensive curriculum for students who plan to transfer to four-year colleges and universities. In addition, the department offers developmental courses taught in a variety of formats. Students can enroll in these courses for personal enrichment and/or to get ready to take courses at the college level. The department offers support for all mathematics students in the Mathematics Center, a facility staffed by faculty and tutors.
Major
The completion of an Associate in Arts degree in mathematics or an Associate in Science degree in mathematics for transfer demonstrates commitment to the field and provides comprehensive preparation for upper-division courses in most professional careers related to mathematics.
Program Student Learning Outcomes
Upon completion of the mathematics program, students will be able to
- Perform arithmetic operations proficiently.
- Demonstrate proficiency in algebra.
- Solve application problems at the level of the course in which they are enrolled.
- Interpret the solution of an application problem and provide an answer appropriate to the context of the problem.
- Demonstrate proficiency in the material of the course in which they are enrolled.
- Use technology in the problem-solving process, when appropriate.
Potential Careers (For Non-Transfer Degree Recipients)
A two-year degree in mathematics equips students with problem-solving skills that employers in many fields find attractive. Some of the jobs that a person with an AS in mathematics could obtain are:
- Accounts payable or receivables clerk
- Assistant to a certified public accountant
- Auditing clerk
- Bank teller
- Bookkeeper
- Clerk in a brokerage firm
- Computer technician
- Insurance sales agent
- Loan processor
- New accounts clerk
- Payroll clerks
- Tutor
Additionally, an AS in mathematics will give students a strong background to continue their education in four-year colleges in any STEM field. Below is a list of some career paths that a student with an AS degree in mathematics could follow.
- Astronomy
- Business Administration
- Chemistry
- Computer Science
- Economy
- Engineering
- Mathematics
- Operations Research
- Physics
- Psychology
- Statistics
- Teaching
ProgramsAssociate in ArtsAssociate in Science for Transfer
 Return to: Program, Degree and Certificate List Return to: Program, Degree and Certificate List
|